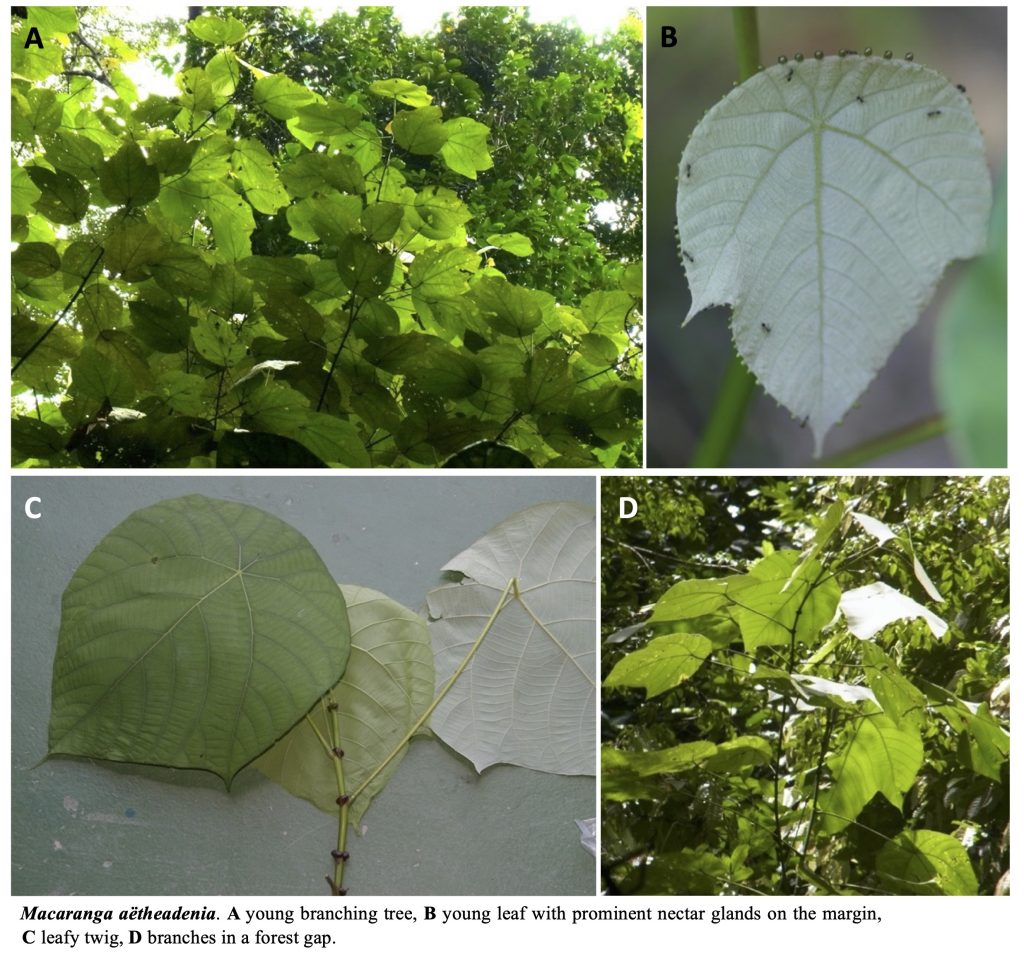
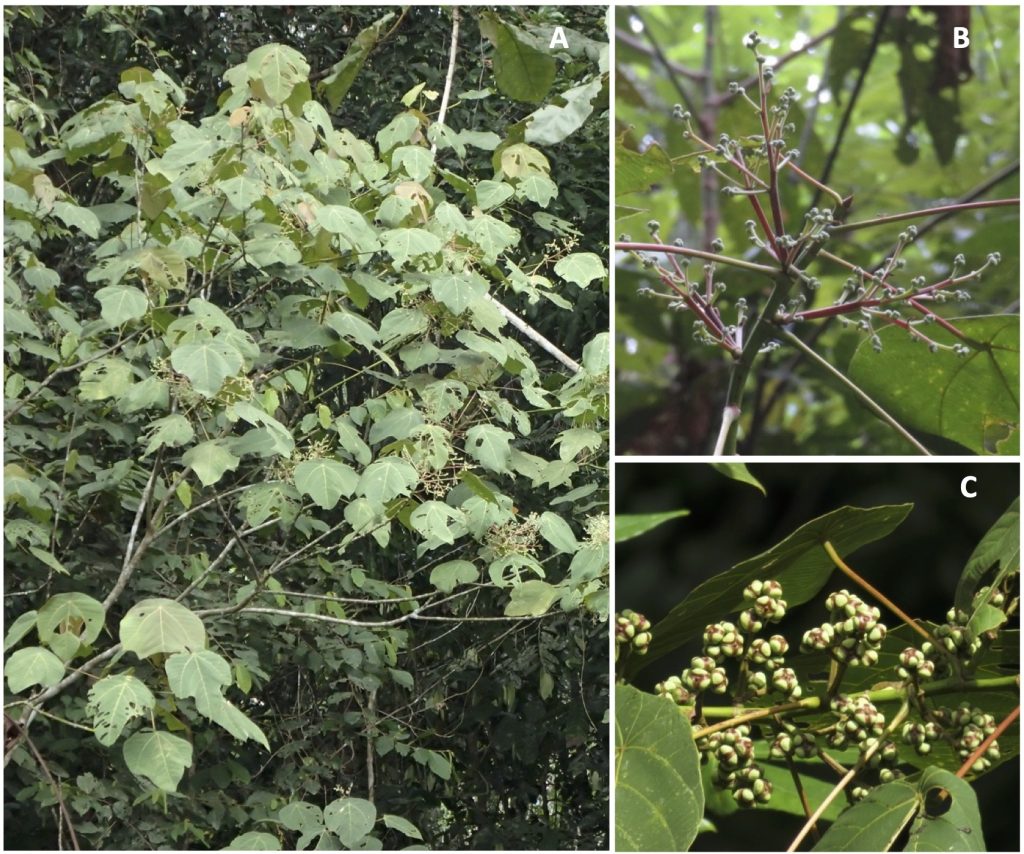
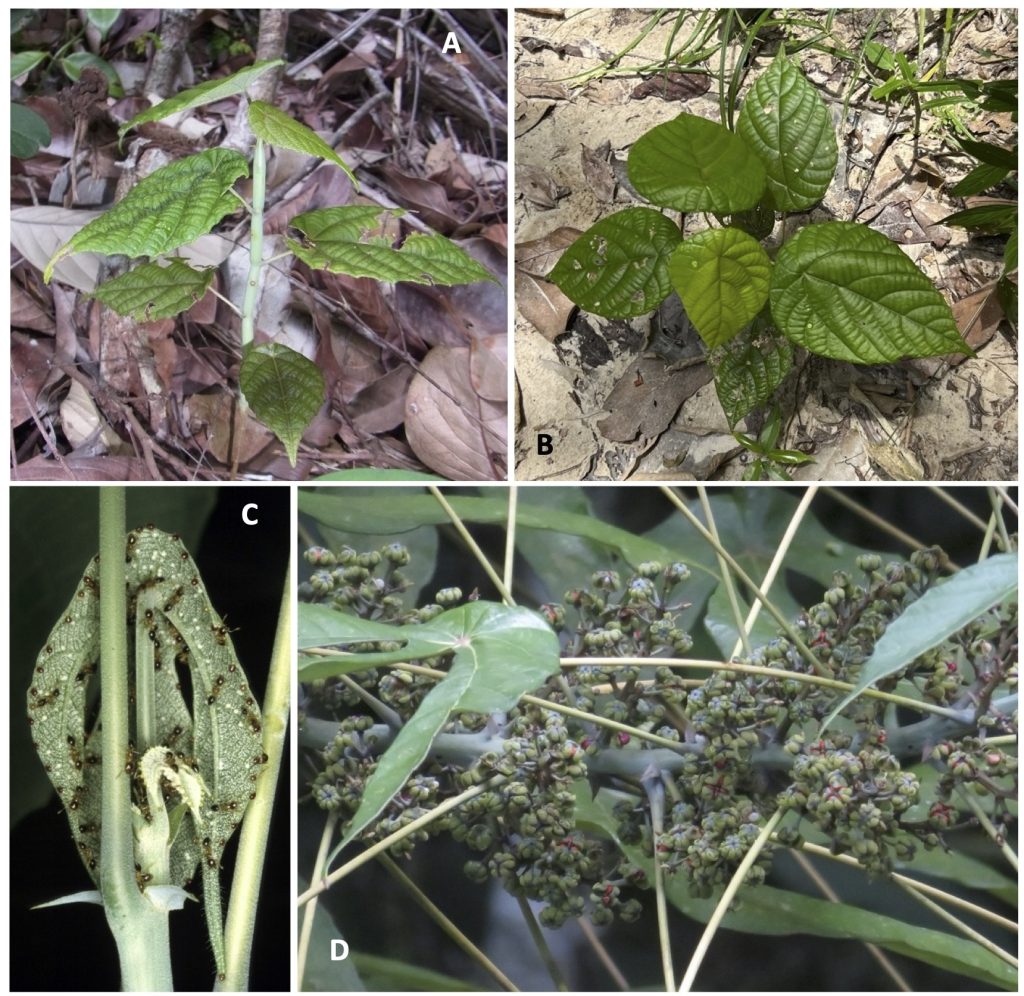
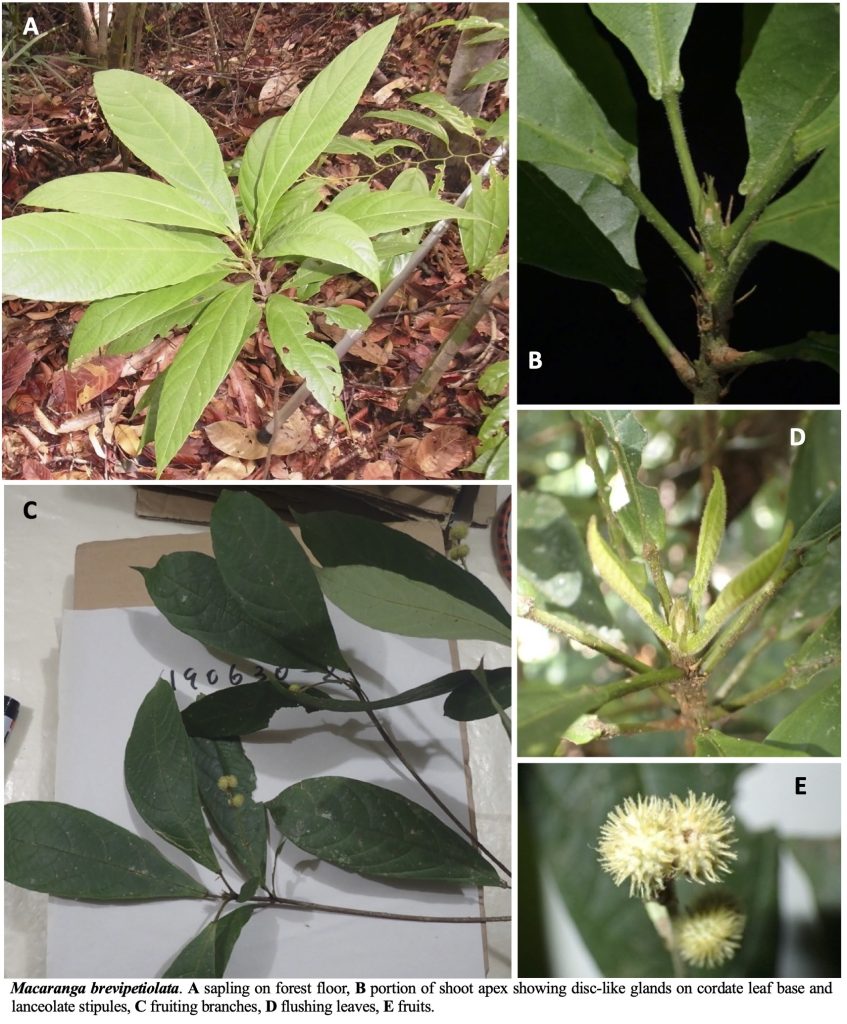
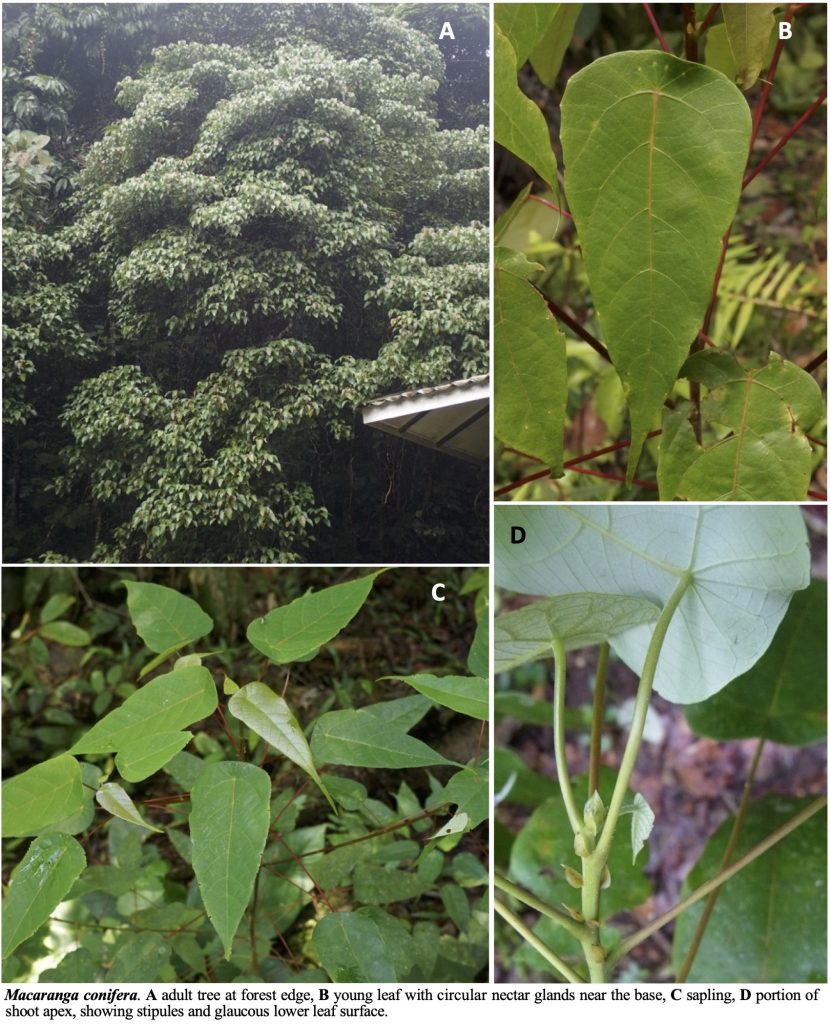
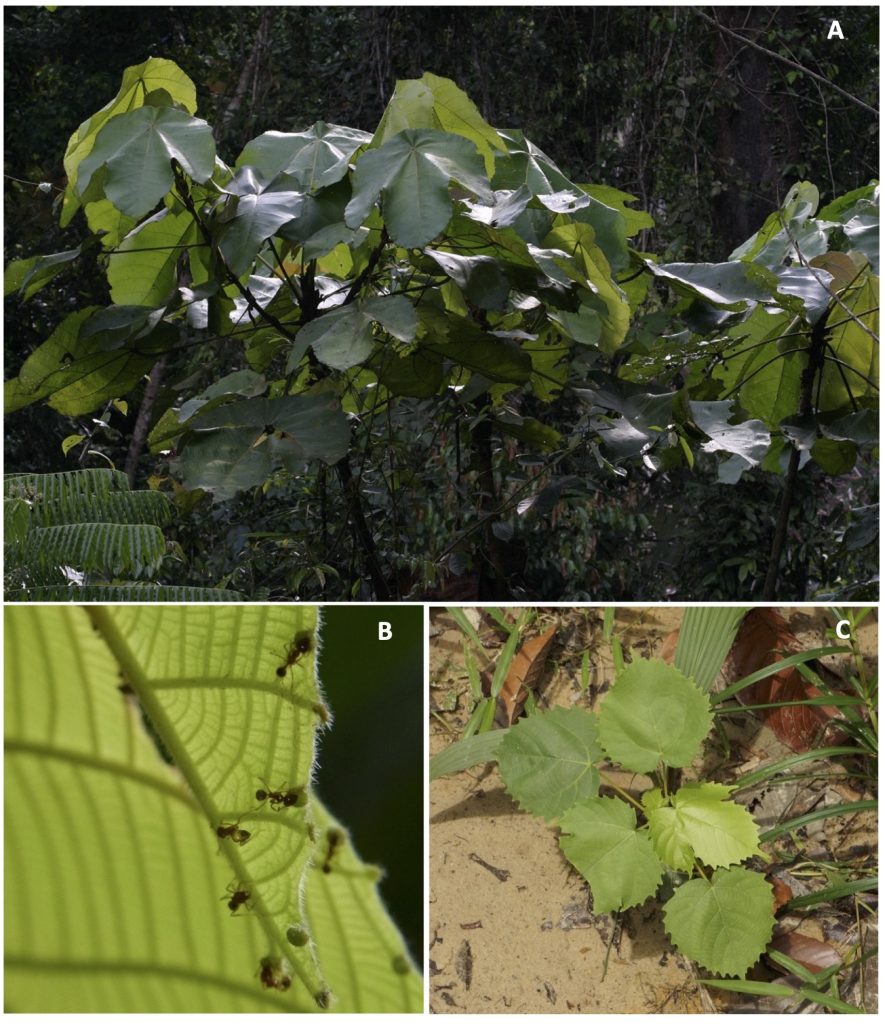
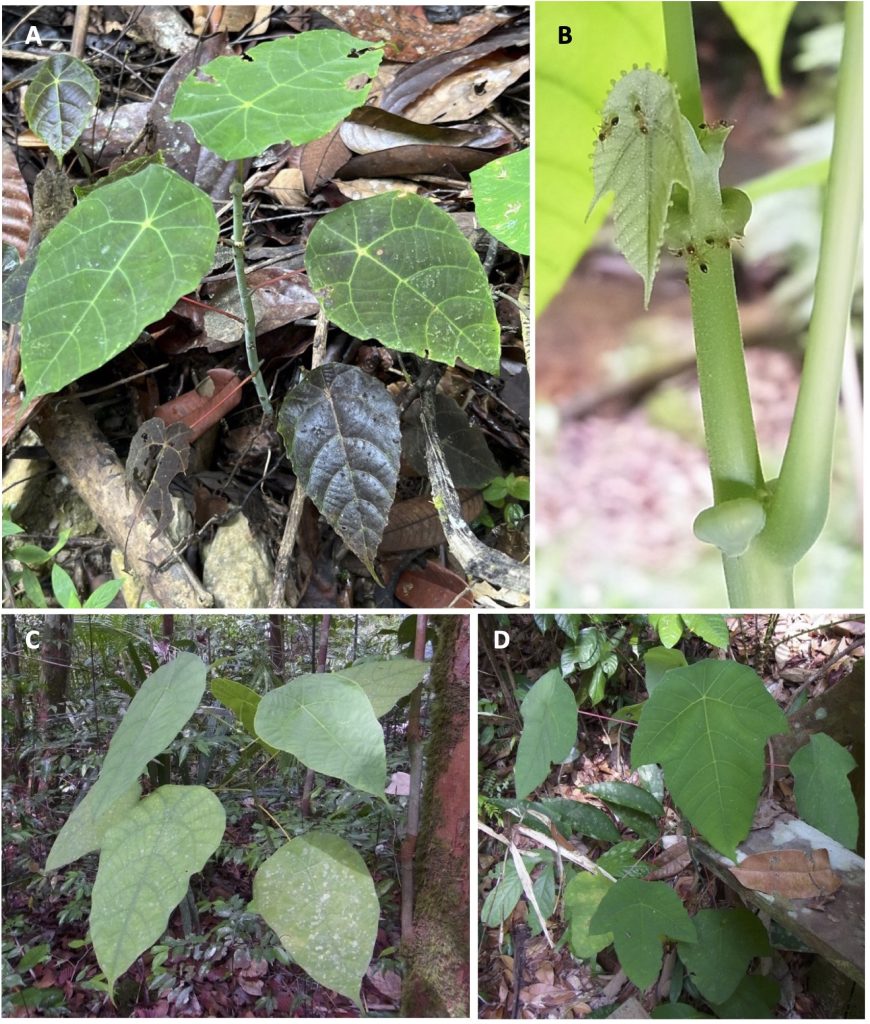
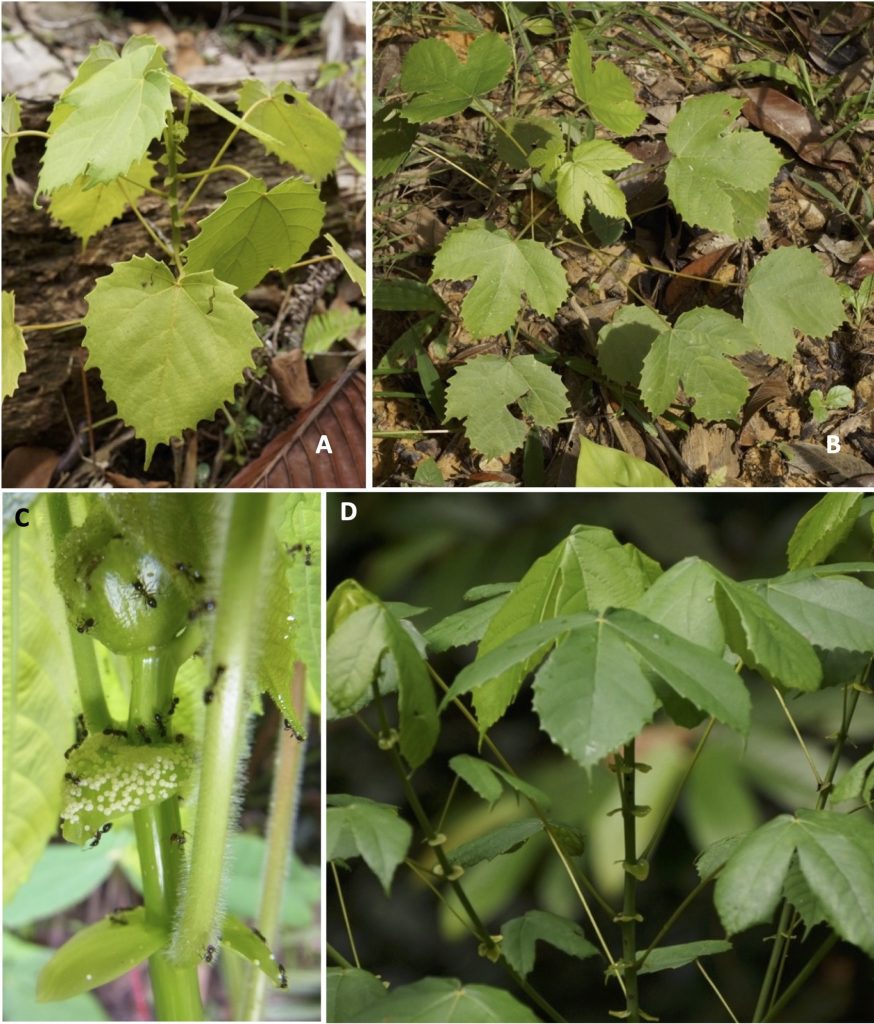
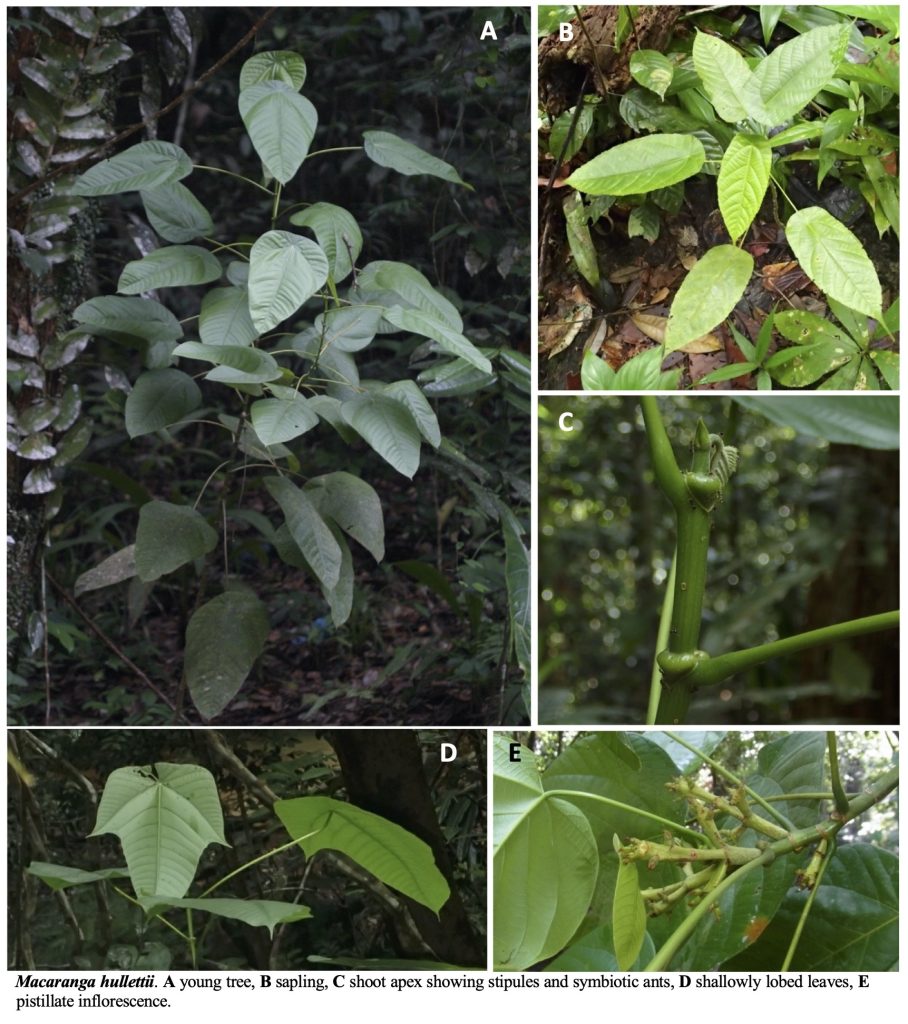
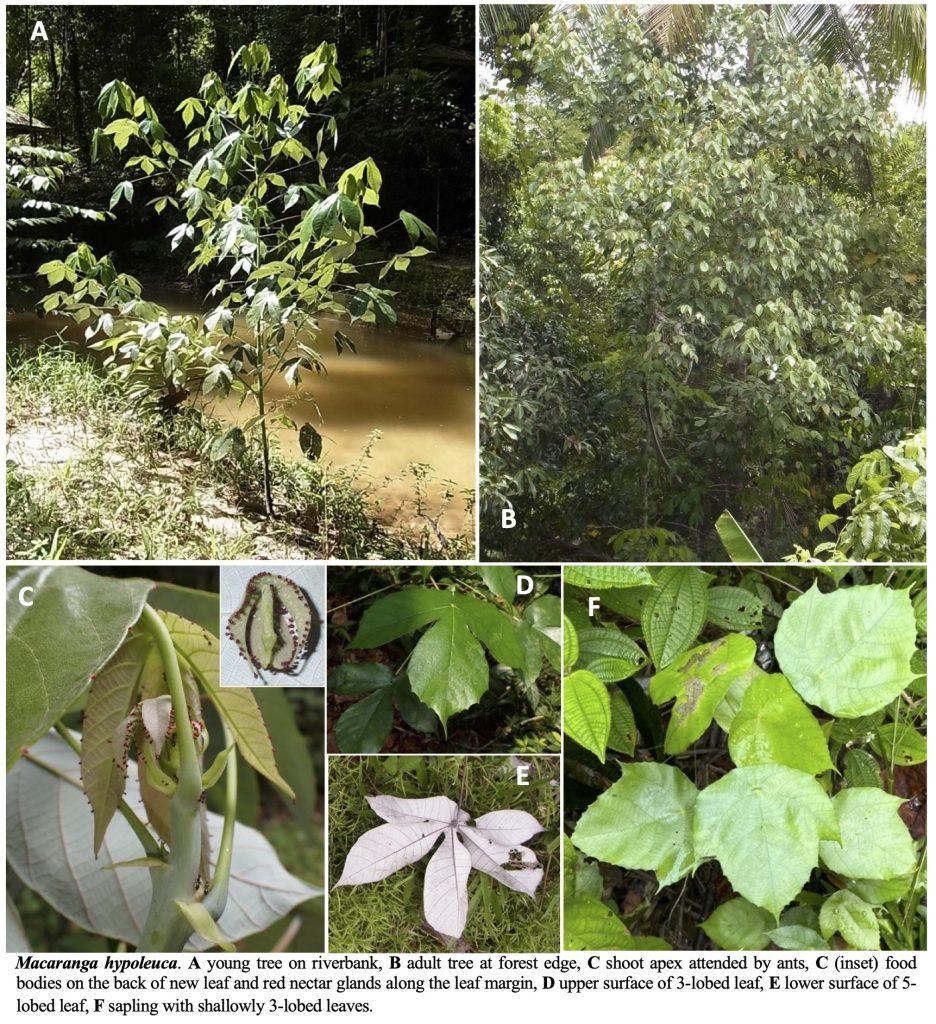
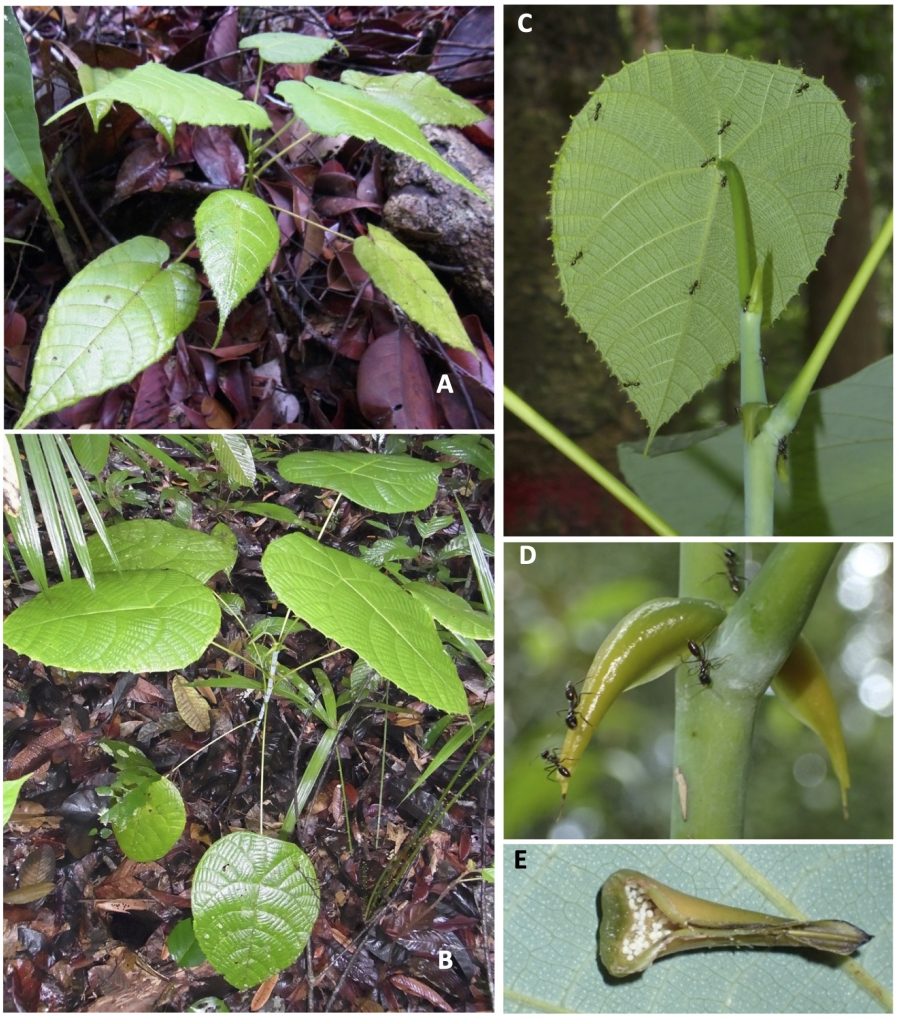
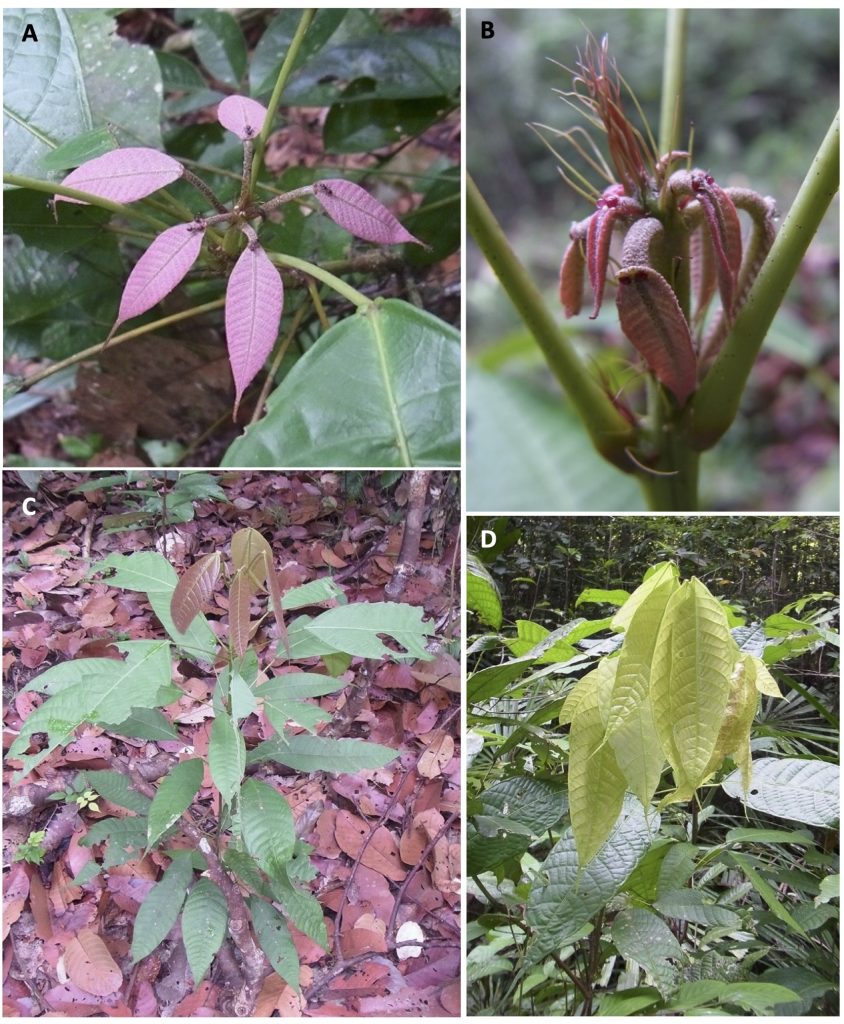
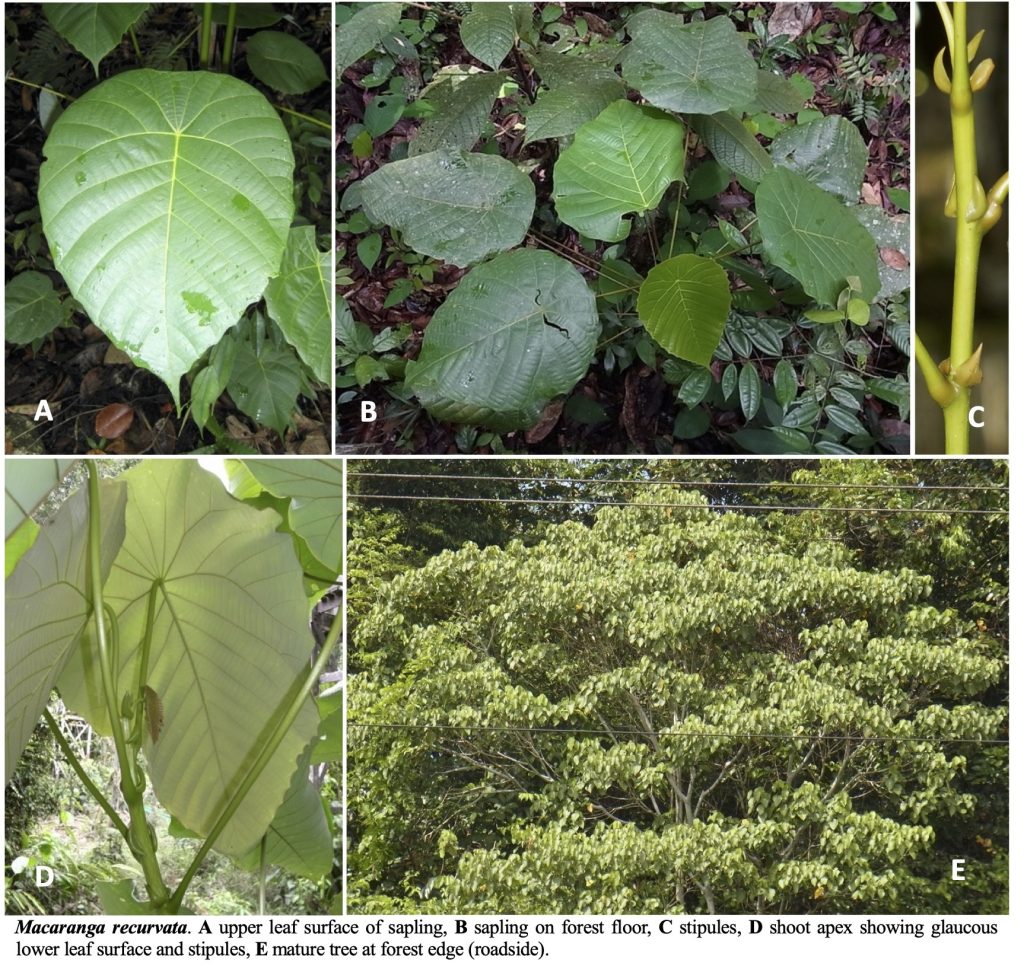
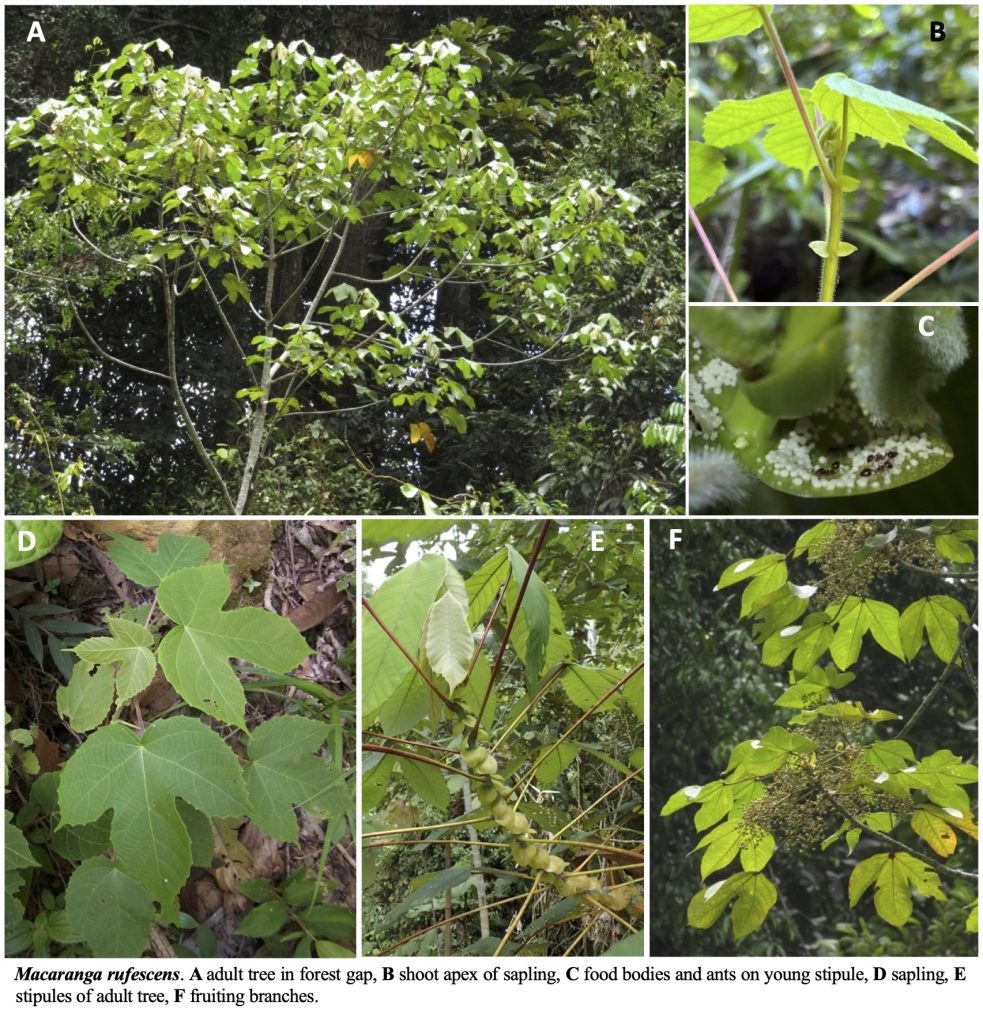
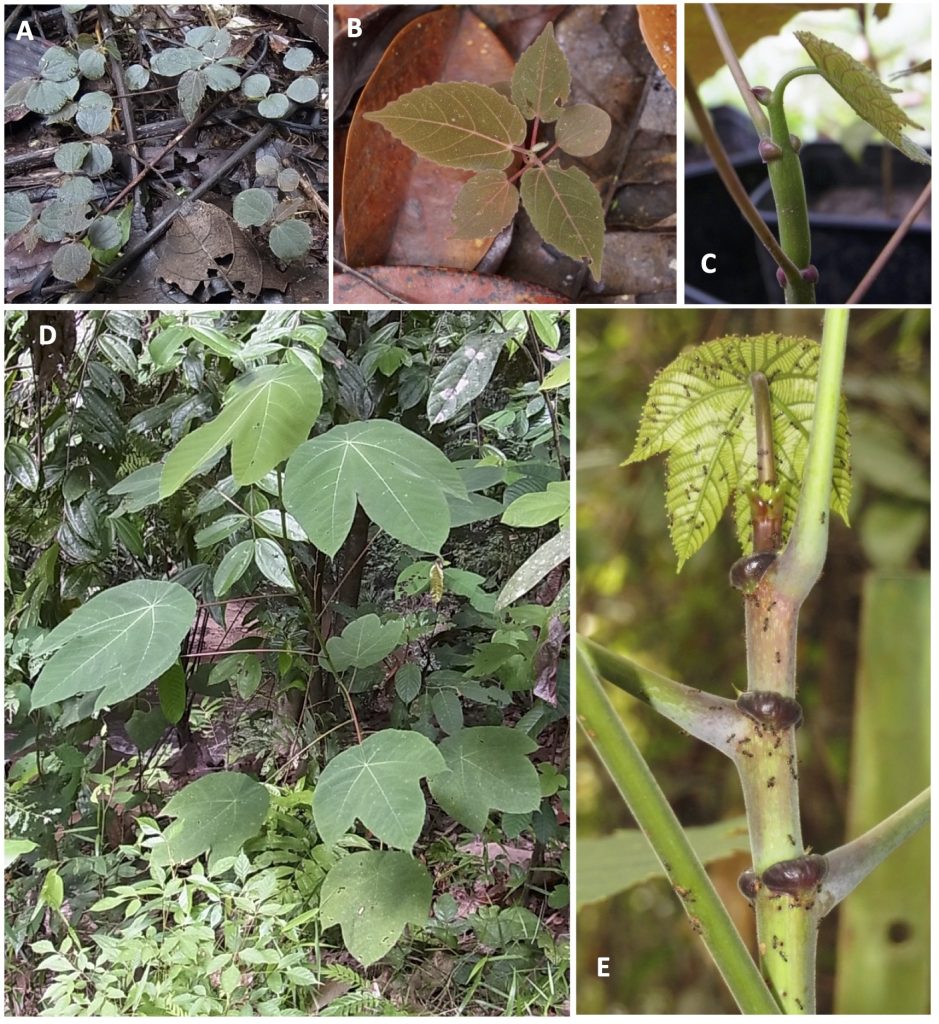
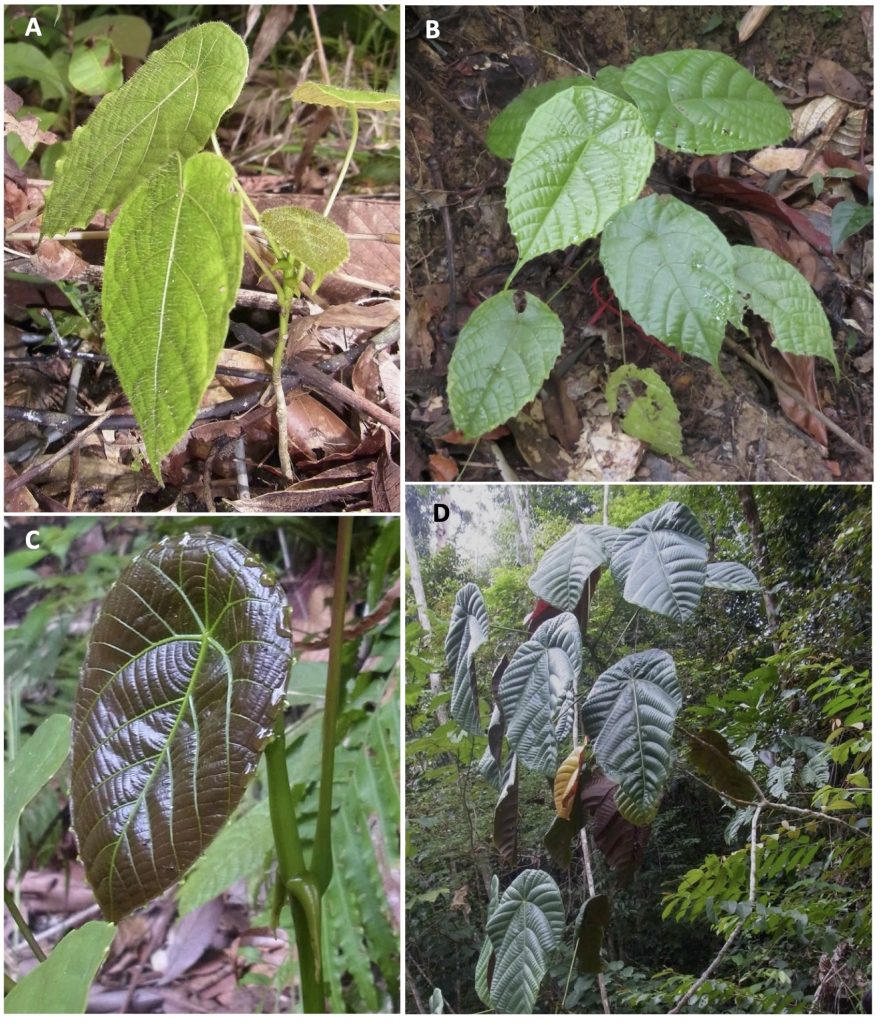
A Guide to Macaranga (Euphorbiaceae) of Lambir Hills National Park, Sarawak, Malaysia
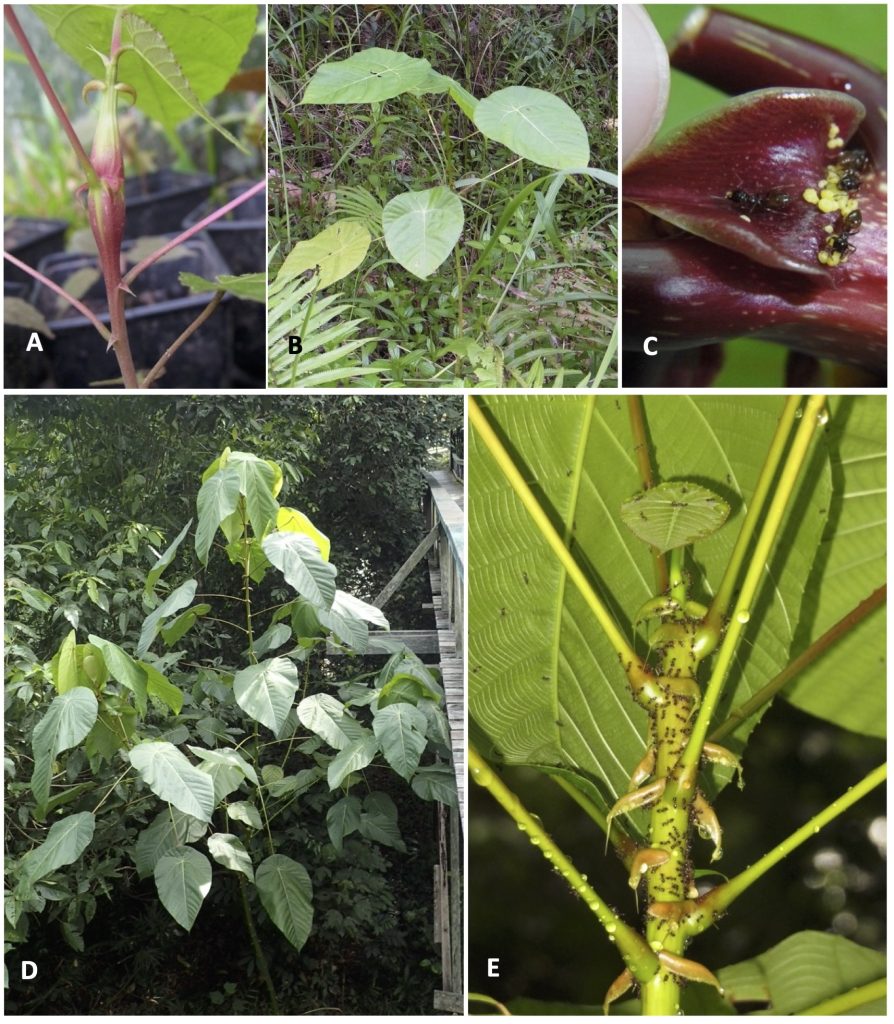
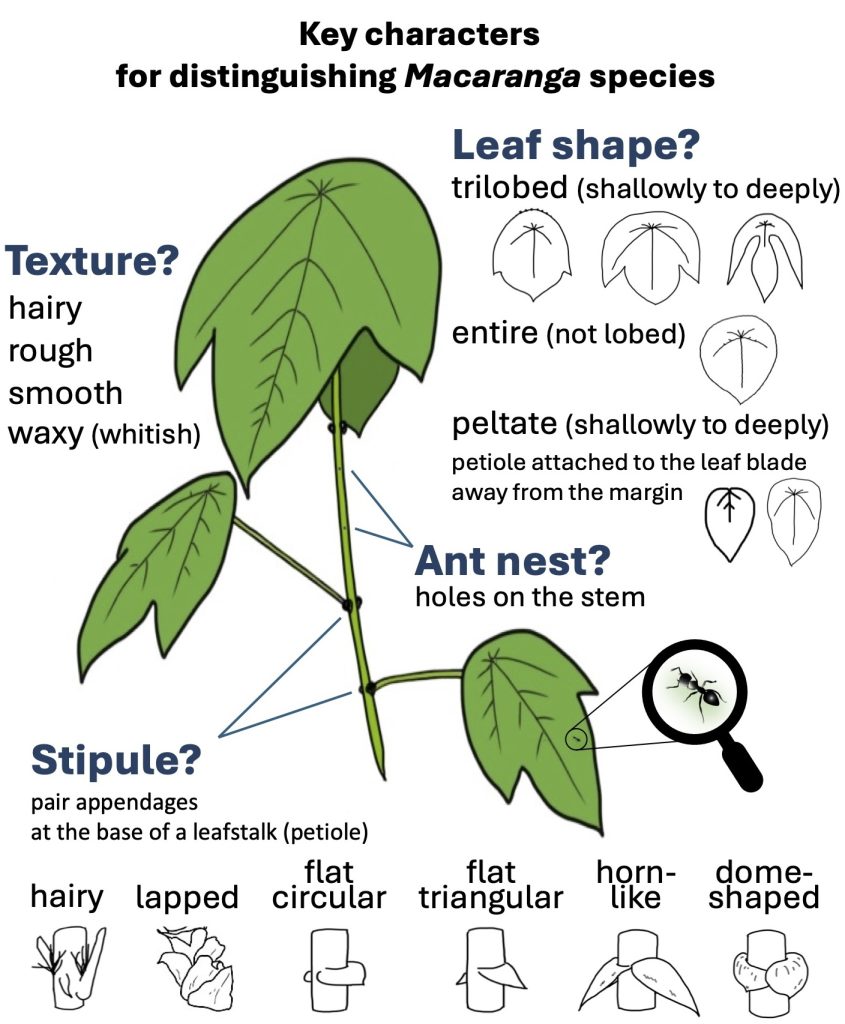
Macaranga Thouars (Euphorbiaceae) is a palaeotropical genus with its greatest diversity in Southeast Asia, particularly in Borneo. Of the 308 species of Macaranga, at least 50 species classified in eight sections/informal species groups of the genus are distributed in Borneo. Most of the species are small to medium-sized trees and early successional species, which are common in forest gaps, on riverbanks, at edges of primary forests, or in secondary and disturbed vegetation. Most Macaranga species are easily recognizable by their large peltate leaves and long petioles.
This genus is also notable for its symbiotic relationship with ants. More than 25 species are “myrmecophytes” or “ant-plants,” which host ant colonies within the hollow stems of the plant. Myrmecophytic Macaranga species provide ants with nesting spaces and food resources, such as extrafloral nectar and food bodies, and, in return, the ants protect the host tree from herbivores, pathogens, and vines. The mutualism presents a superb opportunity to study plant–ant interactions.
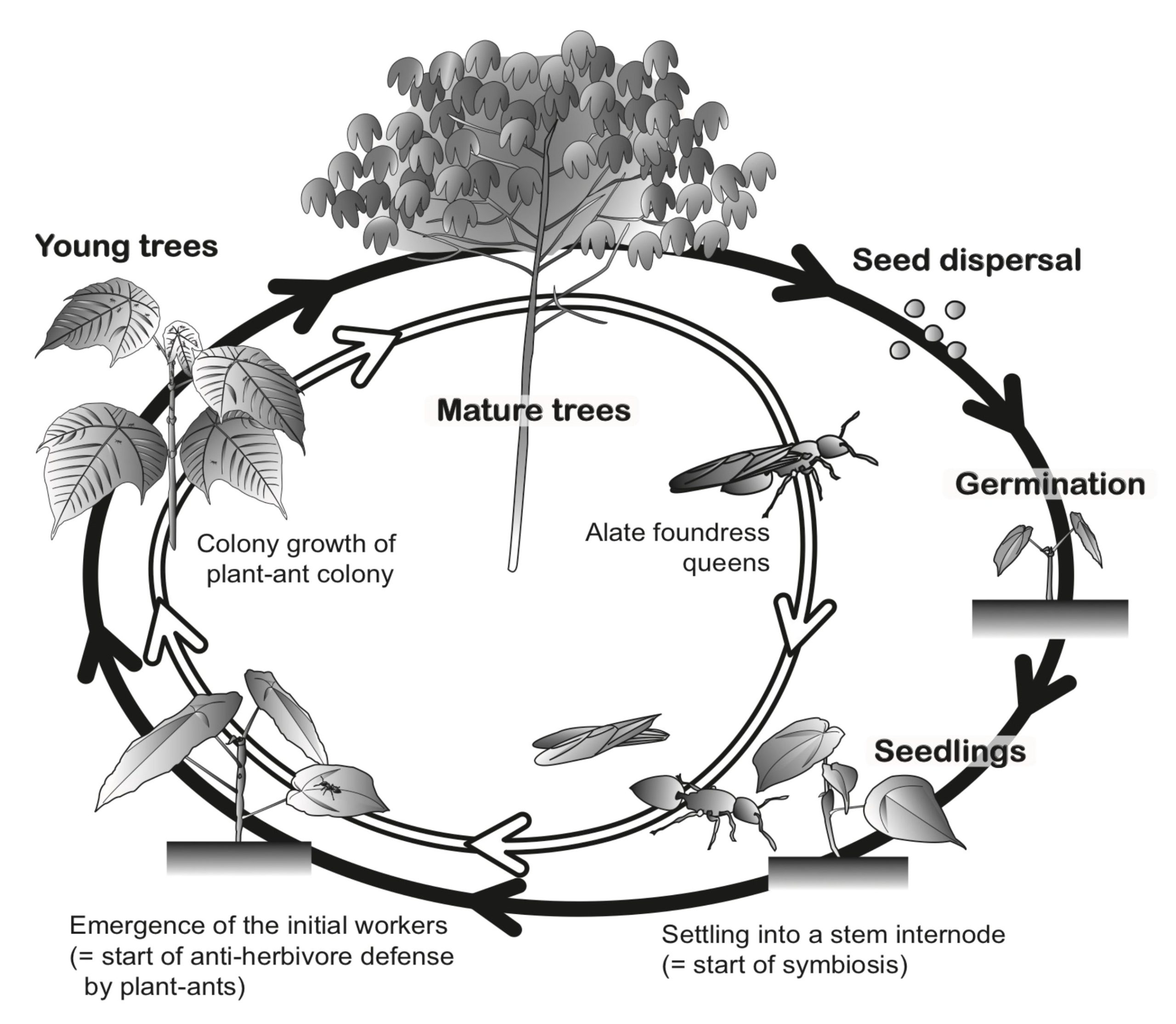
Typical life cycles of Macaranga myrmecophytes (black line) and plant-ant colonies (white line)Shimizu-kaya U, Inui Y, Ueda S, Itino T, Itioka T. 2015. Geographical variation of mutualistic relationships between Macaranga myrmecophytes and their ant partners: research plans in Sarawak. International symposium “Frontier in Tropical Forest Research: Progress in Joint Projects between the Forest Department Sarawak and the Japan Research Consortium for Tropical Forests in Sarawak”
Situated in Sarawak, Malaysia, in northwestern Borneo, the lowland tropical rainforest in Lambir Hills National Park (LHNP) has long been known as an extremely floristically species-rich ecosystem. At least 17 species of Macaranga from five sections or groups are distributed within the park. This comprises almost half the number of known Macaranga species that grow in lowland areas throughout Sarawak and includes 12 myrmecophytic species.
This web guide includes photographs of individual species, and a systematic key to distinguish each Macaranga species found in LHNP together with a brief introduction to their biological traits and ecological preferences. It has been adapted of the following article with permission of the authors and the publisher: Shimizu-kaya U, Itioka T, Tagane S, Tipot E, Gumal MT. 2024. A Guide to Macaranga (Euphorbiaceae) of Lambir Hills National Park, Sarawak, Malaysia. Contribution from the Biological Laboratory, Kyoto University 32: 50-81. Refer to the original article for citation.
For more detailed information on each species, such as morphological characters and distribution areas, consult the references listed below:
- Davies SJ (2001) Systematics of Macaranga sect. Pachystemon and Pruinosa (Euphorbiaceae). Harvard Papers in Botany 6: 371–448.
- Slik JWF, van Welzen PC (2004) Macaranga and Mallotus species of Borneo. Nationaal Herbarium Nederland, Leiden University, Leiden, The Netherlands. https://asianplant.net/MacMalBorneo/. Accessed July 2024.
- Whitmore TC (2008) The Genus Macaranga – a Prodromus. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Richmond.
- Whitmore TC, Coode MJE, Hoffmann P, Davies SJ, Slik JWF, Priyono, van Welzen PC, Takeuchi W (2020) Flora Malesiana: Malesian Euphorbiaceae Descriptions: 66 Macaranga (Euphorbiaceae). https://www.nationaalherbarium.nl/Euphorbs/specM/Macaranga.htm. Accessed July 2024.